Chapter 3 Synchronizing receiver clocks
Arrays with independent receivers need to have their clocks synchronized before telemetry positioning can be done. Positioning requires detection error on the order of a few milliseconds while clock error can be on the order of tens of seconds—in our experience.
kaltoa synchronizes array clocks by breaking down clock error into drift and offset. First, clock error is just the deviation of a target clock from some controller clock. In practice, we select one of our receivers as the controller, of which all other receivers will be calibrated to (for larger arrays, we can specify a chain of control receivers).
- Clock drift is the change of clock error over time for a receiver. This is represented as a vector of clock drift corrections over time for a pair of receivers.
- Clock offset, in kaltoa, refers to a time-independent clock correction which minimizes the difference between the measured and expected sync-tag transmission latency.
Each receiver has a single clock offset value while the (first) controller has a fixed value of
0.
The sync-tag transmission latency is simply the tag detection time minus the emission time in a receiver pair. The expected transmission time is calculated from the distance between the receiver pair. Hence, for clock synchronization to work, we need to know the locations of each receiver in the array.
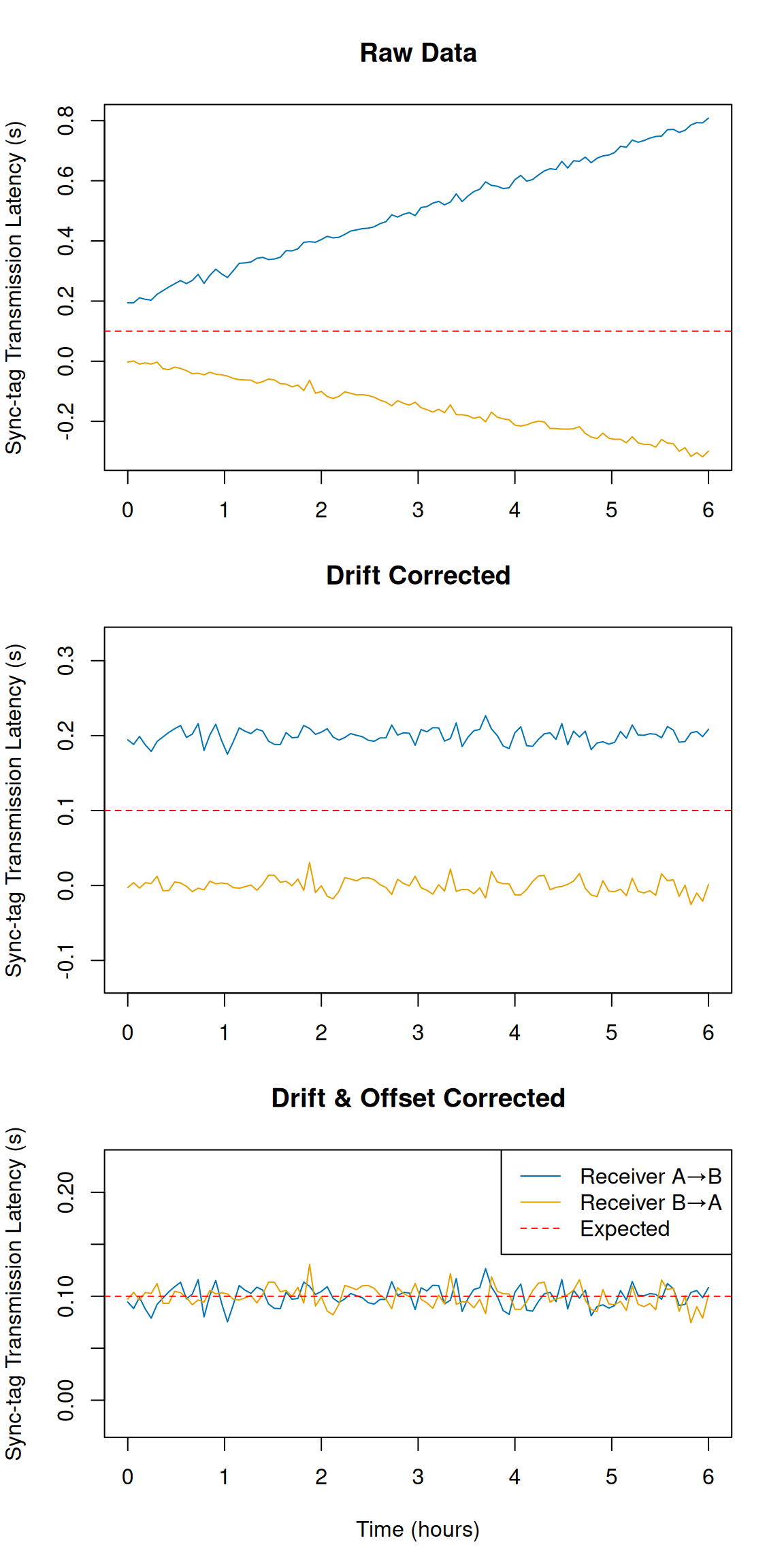
The figure above gives a visual guide of how kaltoa views clock error. The following sections will show how to apply these corrections to your detections data.